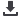
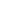
MMSE
≤
20, with severe sensory deficits and behavioral changes
were excluded. Statistical analysis was used SPSS18 package and
conducted socio-demographic analysis and analysis of variance
between the results of the two groups before and after the
intervention. To identify the effect of the intervention from baseline
to post intervention a paired t-test was used. The level of significance
adopted was 5%.
Results:
99 subjects, age 71,8 ± 6,3 (CG) and 71,4 ± 6,6 (IG), male 2
(18,2%) CG and 24 (27,3%) IG, female 9(81,8%) CG and 64 (72,7%) IG,
MMSE 28,45 ± 1,75 CG and 28.72 ± 1.56 (IG). There was significance for
all variables, (SPPB) (POMA-BR), time (seconds) of sitting and standing
without hand support 5x, (FPM) an gait speed the experimental group
and none in the control.
Conclusion:
The exercise protocol was effective to improve the
performance of seniors who submeted to our program.
P-603
Attendance avoidance through app based medication review
J.J.R. Muller, R. McNamara, C. Mitchell.
Imperial College Healthcare Trust,
London, UK
Objectives:
Adverse drug reactions represent a major burden on
healthcare, causing between 3% and 5% of all hospital admissions [1].
This impact is magnified in older patients; studies have shown that up
to 51.3% of older patients were prescribed potentially inappropriate
medications [1]. These findings are highly relevant to Emergency
Medicine with ever increasing emphasis being placed on attendance
avoidance, and increasing numbers of older patients.
Method:
We utilised the STOPP/START criteria [2] and Anticholinergic
burden scoring [3] to assess the drug histories of all patients over
the age of 65 who presented over the course of a year to a major
London A + E department with three common presentations: bleeding,
confusion and falls.
Results:
We found consistently high levels of potentially inappropriate
prescribing with 64% of patients presenting post a fall, 92% with new
confusion and 23% with bleeding, having drug histories that warranted
a medications review. 22% of patients presenting after a fall also had
clinically relevant anticholinergic scores and higher re-attendance
rates than those with low anticholinergic scores.
Conclusion:
We designed a pilot study using a digital app designed by
a Geriatrician to analyse and prompt potential medication changes for
patients admitted to our Clinical Decision Unit with the aim of future
attendance avoidance.
References
[1] Prevalence of potentially inappropriate prescribing in an acutely ill
population of older patients admitted to six European hospitals.
Gallagher
et al.
2011.
[2] Prevention of potentially inappropriate prescribing for elderly
patients: a randomized controlled trial using STOPP/STARTcriteria.
O
’
Mahoney
et al.
2011.
[3] From NHS Scotland Polypharmacy Guidance Oct 2012.
P-604
Data model for the Portuguese national study on the nutritional
status among elderly living in the community and nursing homes
(PEN-3S project): What can be done with it?
G. Gomes
1
, T.M. Madeira
1,2
, C. Peixoto-Plácido
1,2
, N. Santos
1,2
,
A. Bergland
5
, A. Bye
5
, T. Amaral
6
, C. Lopes
7
, V. Alarcão
1,2
, B. Goulão
3
,
N. Mendonça
4
, O. Santos
1,2
, P.J. Nicola
1
, J. Gorjão Clara
1,2
.
1
IMPSP,
Faculdade Medicina, U Lisboa,
2
ISAMB, Faculdade Medicina U Lisboa,
Portugal;
3
University of Aberdeen, Institute of Preventive Medicine,
Scotland;
4
Newcastle University Institute for Ageing, UK;
5
Oslo and
Akershus University College of Applied Sciences, Norway;
6
Faculdade de
Ciências da Nutrição e Alimentação, U Porto,
7
ISPUP, Faculdade Medicina,
U Porto, Portugal
Introduction:
A national community-based assessment of the
psychosocial, functional and nutritional status of elderly people in
the community and at nursing homes is a precious data and analysis
resource for research. We present the PEN-3S design and data model
and discuss potential for research and analysis.
Methods:
Nationally representative cross-sectional survey collected
data through face-to-face structured interviews and anthropometric
measurements. Nursing homes residents and community-dwelling
elderly were randomly selected, from a sample of 1800 participants.
Data regarding sociodemographics, clinical data, nutritional status
(Mini Nutritional Assessment), food insecurity, loneliness (UCLA
loneliness scale), functionality (Lawton and Brody scale), depression
(Geriatric Depression Scale), physical activity (International Physical
Activity Questionnaire), anthropometric measurements, food propen-
sity and 24 h dietary recall were collected, as well as their own nursing
homes characteristics.
Results:
In this study, about 230 variables were collected concerning
the 12 dimensions indicated above, in both settings. We mapped the
information gathered, report data quality, subgroup characteristics
and explore the research potential for analyzing this data and for
comparing the Portuguese reality with data coming from of other
communities and countries studies. For specific areas (social, clinical,
nutritional, psychological and nutritional) we listed key research
questions to be addressed in this study.
Key conclusions:
Large, representative and comprehensive epide-
miological studies are of great importance and a resource for
analyzing and exploring a multitude of research questions. Being
acquainted and discussing its potential will allow for the interested
multidisciplinary research community to better explore and use this
resource.
P-605
Cognitive, physical and nutritional status in Older Adults. Six
month follow up in elderly subjects addressing European
PERsonalised ICT Supported Service for Independent Living and
Active Ageing (PERSSILAA project)
A. Renzullo
1
, L. Barrea
2
, M. Illario
3
, V. Iadicicco
3
, P. De Matteis
3
,
G. Tramontano
3
, P.A. Riccio
1
, V. Zhukovskaya
1
, S. Savastano
1
, A. Colao
1
,
C. Di Somma
4
.
1
Dipartimento di Medicina Clinica e Chirurgia, Unit of
Endocrinology, Federico II University Medical School of Naples, Via Sergio
Pansini 5, 80131 Naples,
2
I.O.S. & COLEMAN Srl, Acerra, Naples,
3
Department of Translational Medical Sciences, Federico II University, and
R&D Unit, Federico II University Hospital,
4
IRCCS SDN, Napoli Via
Gianturco 113, 80143, Naples, Italy
Background:
Senile dementia, bone reduction and malnutrition are
among the major mortality and morbidity in the elderly. Perssilaa is an
European project developing health services to detect and prevent
frailty in older adults by addressing cognitive, physical and nutritional
domains. METHODS: 180 subjects (85% female) 72.5 ± 4.9 aged were
consecutively enrolled. Validated questionnaires: QMCI, MNA, SF12
and EQ5D were used for the assessment of cognitive status, risk of
malnutrition and quality of life. Bone mineral density was assessed by
Quantitative ultrasound (QUS). These parameters were evaluated at
basal and after six month follow up.
Results:
At the baseline, the QMCI, MNA, SF12 and EQ5D was
administered in 110, 117, 120, 115 patients and in 88, 81, 46, 49
patients after six month follow up, respectively. The QMCI score
improved in 53,4% were stable in 37.9% and impaired only in 8.6%
of subjects. The MNA score improved in 49.2% were stable in 29.5% and
impaired in 21.1%. The SF12 score improved in 45.6%, were stable in
6.5% and impaired in 47.8%. The EQ5Dscore improved in 53%,
were stable in 20.4% and impaired in 26.5%. Mean T score was
measured only at baseline and according with T score 17.1% subjects
were osteoporotic, 54.5% osteopenic and 42.8% had a with normal
bone density.
Conclusions:
These preliminary data suggest that tailored health
services that integrate face-to-face and ICT supported tools targeting
community dwelling older adults are effective to detect and prevent
frailty.
Poster presentations / European Geriatric Medicine 7S1 (2016) S29
–
S259
S188