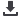
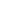
mRankin = <2. Were identified comorbidities in 84.5% of patients and
the complications, the prevalence of anemia was (53.03%) and urinary
tract infections (19.70%). There was a gain in functionality regarding
in admission to the unit in 82.7% and to the previous functional status
of 24.5% (p = .0001). As to mortality we had 0.9% and 82.7% were
discharged to home.
Conclusion:
Our study indicates that co-management of hip fracture
patients by multidisciplinary team is effectiveness in the control of
comorbidities, reduced complications, gains in functionality and low
mortality. The concept should be further developed particularly
among the frail elderly.
P-454
Gender differences in caregiver strain? A post hoc analysis
A.A. Lefebre -van de Fliert, C.M. Tamis, L. Los, M. van Eijk,
W.P. Achterberg.
Leids Universitair Medisch Centrum
Introduction:
After rehabilitation, most stroke survivors are dis-
charged home, where the informal caregivers provide the care that
is needed to function in the home-situation. We hypothesized
that these caregivers experience strain based on functional abilities
as well as neuropsychiatric symptoms of the person they provide
care for.
Methods:
The Caregiver strain Index (CSI), used to determine caregiver
strain, was dichotomized at the cut off of 7/14. Barthel Index (BI) was
used for assessing functional abilities and the neuropsychiatric
Inventory (NPI) was used to assess neuropsychiatric symptoms. Data
were collected 3 months after discharge from geriatric stroke
rehabilitation in patients and their informal caregivers. A multivariate
binary regression model was built to determine the independent
relationship of BI and NPI with caregiver strain.
Results:
Our sample consisted of 72 patients with an average age of 78
years. Thirty-one patients were male. The data showed a significant
interaction for BI and gender, resulting in 2 different models. For males
BI as well as NPI independently related to CSI, with an odds ratio of
0.61 (95% CI 0.40
–
0.94) and 1.32 (95% CI 1.04
–
1.67) respectively. This
was not the case for female stroke survivors. The BI nor the NPI showed
an independent relation with caregiver strain.
Key conclusions:
We found that caregiver strain was determined by
lower functional abilities and higher scores on the NPI, but this was
only the case in male stroke survivors. We hypothesize that most male
stroke survivors will have female spouses, putting these caregivers at
higher risk for greater strain.
P-455
New technologies in rehabilitation of upper limbs
R. López-Liria
1
, J.J. Gutiérrez-Giménez
1
, F.A. Vega-Ramírez
1
,
P. Rocamora-Pérez
1
.
1
University of Almería. Almería. Spain
Objective:
To show the latest trends in technology for the rehabilita-
tion of the upper limb, its impact on research and clinical practice and
the current lines of development.
Method:
Systematic review. The search for articles was conducted
in the databases PudMed and PEDro, using as restrictors date of
publication in the last 10 years and randomized controlled trials. The
selection criteria were: articles in which the effects of new technolo-
gies in patients with upper limb functional deficits were evaluated.
Only those studies that referenced in the title to virtual reality, robotics
and telemedicine/remote rehabilitation, telerehabilitation or new
technology were included in the review.
Results:
17 articles were selected, in which different treatments based
on the use of new technologies were applied. Almost all analyzed
articles described the advantages of using new technologies in the
treatment of patients who had suffered a CVD, with the exception of
a study that referred to humerus fracture treatment. Two of them
focused on virtual reality, 7 were related to robotics, 3 addressed the
issue of telerehabilitation, and 5 considered a combination of devices.
The variables under study were: main motor function, range of motion
and ability to perform activities of daily living. The scales used for
the assessment were the Fugl-Meyer, the Action Research Arm Test, a
scale to measure the range of motion and the Barthel index.
Conclusion:
The use of new technologies appears to be effective in
the recovery of upper limb function, being adaptable to each case,
increasing patient
’
s adherence to treatment and allowing assistance
whatever the location of the patient.
P-456
Chronic diseases in RITH (rehabilitation in the home): a cross-
sectional descriptive study
R. López-Liria
1
, F.A. Vega-Ramírez
1
, P. Rocamora-Pérez
1
, M.I. Segura-
Luján
1
.
1
University of Almería. Almería. Spain
Objective:
To describe the most prevalent disorders in chronic
patients referred to RITH (Rehabilitation in the home) in Almería
province (South Spain).
Methods:
We carried out a cross-sectional descriptive study to
describe the home care provided, the characteristics of its imple-
mentation, and its results on patients and their functional
independence.
Results:
The main diagnoses were motor impairment, hip fracture and
replacement, stroke, knee replacement, chronic obstructive pulmon-
ary disease and Alzheimer
’
s disease. In relation to the descriptive
study about RITH developed in Almería province, it was shown that the
aim of this service (bring the physiotherapy service to the home) is to
fulfill the social and health needs of those patients with functional
limitations due to different diseases, for whom the transfer from their
home to the rehabilitation center is not only difficult and highly cost,
but also stressing and tiring for the patients themselves, with risk of
new comorbidities. In addition, it was proved that this service
improved the functional ability of the patients, according to the
Barthel Index. The effect in user
’
s satisfaction confirms the effective-
ness of this service (as users would ask for this service again in the
future), and provides us with results criteria in the terms of the person
that receives the service.
Conclusions:
Innovative approaches in the management of chronic
diseases have become a basic tool for decision making in healthcare
systems, in order to prevent looses in quality of life and personal
autonomy related with disability.
P-457
Elderly functional assessment outcomes: two years analysis of a
tertiary hospital population sent to long-term care
M.M. Luís, A.A. Sousa, R. Veríssimo, A. Oliveira.
CHVNGE
Background:
Functional capacity refers to autonomy in perform-
ing activities of daily living (ADL) that predict mortality and hospi-
talization of dependent older people. We conducted a 2-year
retrospective cohort study of elderly living in long-term care faci-
lities (LTC), aiming to assess: functional capacity at discharge using the
Katz scale (KZ), its association with readmission to acute care and
mortality.
Methods:
Participants were the referenced patients to National
Network of Long-Term Integrated Care [RNCCI] from January 2013
–
December 2014. The KZ was stratified and applied on discharge.
Statistical analysis utilized chi-squared for pvalue < 0.05 and relative
risk.
Results:
387 patients were referenced to RNCCI, and 81.4% (315/387)
were identified as elders (age
≥
65 years), 58.1% of the patients were
females, the median age was 80 and interquartile range 68
–
84 years.
When stratifying using the KZ: minimal change in functionality in 1.3%
[n = 5], moderate change in 50.6% [n = 196] and total dependence in
48.1% [n = 286]. The overall mortality in RNCCI was 151 (39%). Bivariate
analysis related to total dependence: the mortality was 1.94 (95% CI:
1.58
–
2.38), and readmission ratewas 1.34 (1.06
–
1.69). The older group
is not associated with mortality, readmission and total dependence.
Nevertheless, the older with total dependence is associated to
mortality: 2.11 (CI 1.68
–
2.71), and readmission: 1.54 (CI 1.01
–
2.51),
respectively.
Poster presentations / European Geriatric Medicine 7S1 (2016) S29
–
S259
S150