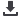
(p = 0.001). In logistic regression analysis adjusted for age and sex,
the risk of malnutrition was associated with increase in NTproBNP
concentration (per quartile)
–
OR 2.23; 95%CI 1.37
–
3.63; p = 0.001.
NTproBNP concentration in 4th quartile was associated with almost
8 times higher risk of malnutrition (OR = 7.9; 95%CI 1.79
–
34.98;
p = 0.006) as compared to the lowest concentration. With increase of
NTproBNP by 100 pg/mL the risk of malnutrition was higher by 3%.
Conclusions:
In the elderly, there is a strong correlation of NT-proBNP
level with the risk of malnutrition and fat tissue.
P-530
Appropriateness of prescribing in nursing home residents with
impaired renal function
G. Strauven
1
, L. Kesters
1
, E. Vanderheiden
1
, L. Verhelst
1
, K. Abdellaoui
2
,
P. Anrys
2
, B. Bammens
3
, A. Spinewine
2
, V. Foulon
1
.
1
Department of
Pharmaceutical and Pharmacological Sciences, KU Leuven, Leuven,
2
Université catholique de Louvain, Louvain Drug Research Institute,
Clinical Pharmacy Research Group, Brussels,
3
Department of
Immunology and Microbiology, KU Leuven, Laboratory of Nephrology,
Leuven, Belgium
Introduction:
The overall aim was to investigate the appropriateness
of prescribing in nursing home residents (NHRs) with impaired renal
function.
Methods:
Data were obtained from the Come-On study, a cluster
controlled trial in 54 Belgian nursing homes (NH), including 1,886
residents (70.4% female). A cross-sectional analysis of baseline data
was performed. Data relative to renal function included the latest value
of the eGFR using the MDRD formula. NHRs with an impaired renal
function were categorized into five stages (KDOQI classification).
According to a consensus document, based on existing guidelines,
potentially inappropriate medicines of NHRs with stage 3 and 4 were
classified as contraindicated, inappropriately or appropriately dose-
adapted.
Results:
Data about eGFR were lacking for 48.5% of NHRs. According
to the available data, the prevalence of stage 3 and 4 CKD was 36.7%
and 5.2% respectively. Based on the consensus document, 996
drugs used by stage 3 NHRs required further attention. Fifteen drugs
(1.5%) were identified as contraindicated and 143 drugs (14.4%) were
classified as inappropriately dose-adjusted. In stage 4, 158 drugs were
further evaluated; 18 (11.4%) were contraindicated and 28 (17.7%)
were inappropriately dose-adjusted.
Key conclusions:
For almost half of NHRs, data on eGFR were lacking.
A systematic determination of eGFR should be implemented to allow
for an appropriate management of CKD in Belgian NHs. The results
demonstrate potentially inappropriate prescribing in NHRs with CKD.
Further research should reveal whether some of the discrepancies can
be justified by patient-specific factors.
P-531
Self-rated health and mortality in the Polish elderly
–
PolSenior
project
A. Szybalska
1
, P. Slusarczyk
1
, A. Skalska
2
, K. Broczek
3
, M. Puzianowska-
Kuznicka
4,5
, M. Mossakowska
1
.
1
International Institute of Molecular and
Cell Biology in Warsaw, Warsaw,
2
Jagiellonian University Medical College,
Cracow,
3
Medical University of Warsaw,
4
Mossakowski Medical Research
Centre, Polish Academy of Sciences,
5
Medical Centre of Postgraduate
Education, Warsaw, Poland
Objectives:
Prognostic value of self-rated health (SRH) on elderly
mortality was observed in many surveys. We analyzed this association
in a representative cohort of the Polish elderly.
Methods:
The PolSenior project was conducted between 2007 and
2012 in a sample of 2,412 females and 2,567 males aged 65 years and
over. Evaluation of SRH was performed in respondents with preserved
cognitive function and measured using Visual Analog Scale (range
0
–
10 points), where 0 meant the worst and 10 the best imaginable
health status. The score of 0
–
3 points was interpreted as poor, 4
–
6 as
fair, and 7
–
10 as good SRH. Socio-economic factors, functional status,
vision and hearing acuity, morbidity and life-style factors were also
accounted for.
Results:
During the 5-year period, 730 females (30%) and 1,009 males
(39%) have died. Significant hazard ratios for all-cause mortality were
observed for females and males with poor (HR 2.48, 95%CI [1.83
–
3.37];
HR 2.62, 95%CI [2.04
–
3.36], respectively), as well as thosewith fair SRH
(HR 1.29, 95%CI [1.03
–
1.60]; HR 1.29, 95%CI [1.10
–
1.52], respectively)
as compared to those with good SRH. Cox proportional hazards
regression model adjusted for all covariates confirmed that SRH was
associated with mortality in females, but not in males. Significant
differences in the risk of mortality were observed only between
females with poor and good SRH (HR 1.77, 95%CI [1.11
–
2.82]).
Conclusion:
SRH may be a valid predictor of all-cause mortality in
elderly females, but not in males. Implemented under publicly-funded
project no. PBZ-MEIN-9/2/2006, Ministry of Science and Higher
Education.
P-532
Acute coronary syndrome in octogenarian patients: renal function
as a determinant factor in their treatment
J. Urmeneta Ulloa, M. Lasala Alastuey, C. López Perales, I. Molina Borao,
E. Sánchez Insa, J.C. Porres Azpiroz, P. Auquilla Clavijo, I. Calvo
Cebollero.
U.H. Miguel Servet
Introduction and objective:
The worsening of renal function (RF) in
context of an ACS has been described as a deleterious factor in the
prognosis, associating more cardiovascular events and an increase
in morbi-mortality. Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is considered a
limiting aspect for an interventionist attitude in the ACS, being more
restrictive in the elderly. Our objective was to determine the
significance of the RF in the decision-making in octogenarians with
ACS, as well as analyze the factors related to its worsening.
Methods:
We included 300 consecutive patients with ACS
≥
80 years
treated in our hospital (2013
–
2015). Multivariate statistical analysis
with SPSS stadistics 18. GFR determined using Cockcroft-Gault
formula and subclassified by stages (CKD1 with GFR > 90 mL/min;
CKD2 60
–
90 mL/min, CKD3 30
–
60 mL/min, CKD 15
–
30 mL/min and
CKD5 <15 mL/min).
Results:
Mean age of 85.42 ± 4.108 years. 58% males; 80% hyper-
tension; 66.7% diabetic and 41.3% dyslipidemia. 18% with cognitive
impairment and 48.1% high Charlson comorbidity index (ChI)
(6.974 ± 2.054 (IC 95% 6.7
–
7.2)). NSTEMI the most frequent form of
presentation (57.7%), followed by STEMI (25.3%) and unstable
angina (17%); with a 56.7% of invasive management. On admission,
the majority have CKD 2 or 3 (CKD1 8%, CKD2 25%, CKD3 49.5%,
CKD4 14.4% and CKD5 3%); with GFR medium of 52.4 ± 25.6 mL/min
(CI 95% 49.5
–
55.3) worsening during hospitalization up to GFR
medium of 44.16 ± 21.9 mL/min (CI 95% 41.6
–
46.6). Resulted in a
progression in the GFR stage at 25.1% (CKD1 3%, CKD2 22.7%, CKD3
44.1%, CKD4 23.4%, and CKD5 6,7%). Variables affecting the worsening
of RF are: female sex (p = 0.049), hypertension (p = 0.009), high ChI
(p = 0.001), coronary angiography performed (p < 0.001), develop-
ment of shock during hospitalization (p < 0.001) and HF (p < 0.001).
Not related to kinds of ACS, number of vessels involved, type of stent as
well as complete revascularization. The worsening of the RF had no
effect on survival in our serie.
Conclusions:
The main factors in the worsening of the RF in
octogenarians with ACS are hypertension, elevated ChI, shock, HF
and coronary angiography performed. Neither kinds of ACS, number of
vessels involved, type of stent or perform a complete revascularization
influenced in renal impairment.
P-533
Implantable loop recorder in cryptogenic stroke: a cardio-geriatric
experience
S. Venzo
1
, M. Rafanelli
1
, E. Schipani
1
, A. Ceccofiglio
1
, F. Tesi
1
, G. Rivasi
1
,
N. Marchionni
1
, A. Ungar
1
.
1
Syncope Unit, Department of Geriatric,
University of Florence, Florence, Italy
Poster presentations / European Geriatric Medicine 7S1 (2016) S29
–
S259
S169